Looking to start an E-commerce platform? Check these details before you start!
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services, or the transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic network, primarily the internet. These business transactions occur either as business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), consumer-to-consumer or consumer-to-business. The terms e-commerce and e-business are often used interchangeably. The term e-tail is also sometimes used in reference to the transactional processes for online shopping.
“You can’t just open a website & expect people to flood in. If you really want to succeed you have to create traffic”.
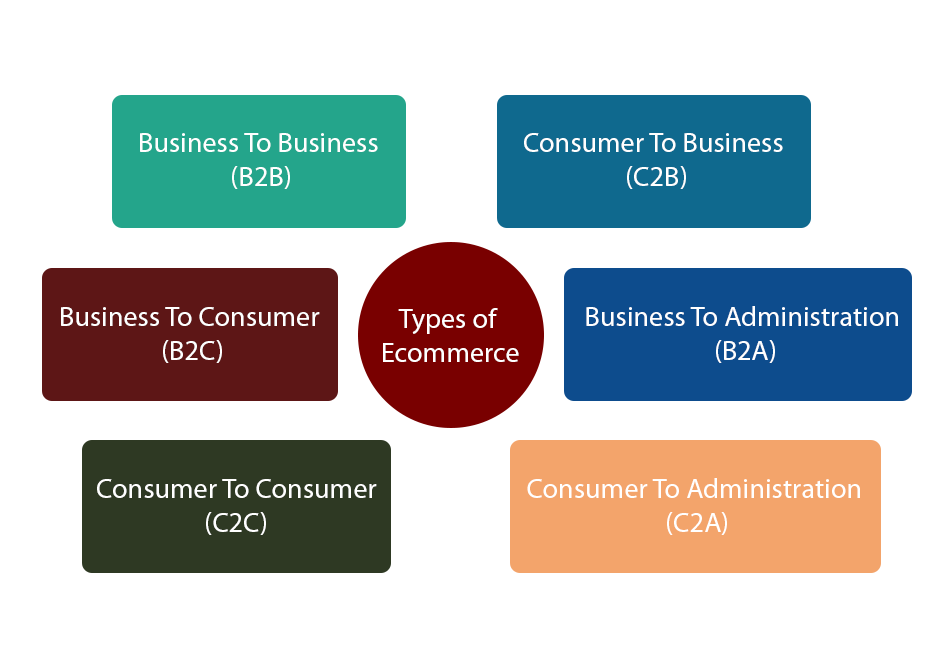
Types of e-commerce
e-commerce refers to the electronic exchange of products, services or information between businesses rather than between businesses and consumers. Examples include online directories and product and supply exchange websites that allow businesses to search for products, services and information and to initiate transactions through e-procurement interfaces.
is the retail part of e-commerce on the internet. It is when businesses sell products, services or information directly to consumers.
is a type of e-commerce in which consumers trade products, services and information with each other online. These transactions are generally conducted through a third party that provides an online platform on which the transactions are carried out.
is a type of e-commerce in which consumers make their products and services available online for companies to bid on and purchase. This is the opposite of the traditional commerce model of B2C.
refers to transactions conducted online between companies and public administration or government bodies. Many branches of government are dependent on e-services or products in one way or another, especially when it comes to legal documents, registers, social security, fiscals and employment. Businesses can supply these electronically. B2A services have grown considerably in recent years as investments have been made in e-government capabilities.
refers to transactions conducted online between individual consumers and public administration or government bodies. The government rarely buys products or services from citizens, but individuals frequently use electronic means in the following areas:
- disseminating information, distance learning/online lectures, etc.
- distributing information, making payments, etc.
- filing tax returns, making payments, etc.
- making appointments, providing information about illnesses, making health services payments, etc.
Basic plans to start E commerce business:
- Select a product to sell/Set up your business
- Identify KPIs for your business.
- Acquiring customers.
- Market extensively.
- Collect feedback.
Select a product to sell:
- Find a product to sell
- Evaluate your product
- Conduct market research
- Obtain your product
- Prepare a business plan
- Sell some samples to attract the customer
Set up your business:
- Find a name & create an attracting logo
- Structure your website
- Build your store that fulfill customer needs
- Select a sales channel
“You should learn from your competitor but never copy. Copy & you die. Always thinks out of the box”.
Benefits of e-commerce
The benefits of e-commerce include its around-the-clock availability, the speed of access, the wide availability of goods and services for the consumer, easy accessibility and international reach.
- Aside from outages or scheduled maintenance, e-commerce sites are available 24x7, allowing visitors to browse and shop at any time. Bricks and mortar businesses tend to open for a fixed amount of hours and may even close entirely on certain days.
- While shoppers in a physical store can be slowed by crowds, e-commerce sites run quickly, which is determined by compute and bandwidth considerations on both consumer device and e-commerce site. Product pages and shopping cart pages load in a few seconds or less. An e-commerce transaction can comprise a few clicks and take less than five minutes.
- Amazon’s first slogan was “Earth’s Biggest Bookstore.” They could make this claim because they were an e-commerce site and not a physical store that had to stock each book on its shelves. E-commerce enables brands to make a wide array of products available, which are then shipped from a warehouse after a purchase is made.
- Customers shopping a physical store may have a hard time determining which aisle a particular product is in. In e-commerce, visitors can browse product category pages and use the site search feature the find the product immediately.
- Pure play e-commerce businesses avoid the cost associated with physical stores, such as rent, inventory and cashiers, although they may incur shipping and warehouse costs.
- E-commerce sites can track visitors’ browse, search and purchase history. They can leverage this data to present useful and personalized product recommendation. Examples include the sections of Amazon product pages labeled “Frequently bought together” and “Customers who viewed this item also viewed.”
Disadvantages of e-commerce
The perceived downside of e-commerce include sometimes limited customer service, consumers not being able to see or touch a product prior to purchase and the wait time for product shipping.
- If a customer has a question or issue in a physical store, he or she can see a clerk, cashier or store manager for help. In an e-commerce store, customer service may be limited: the site may only provide support during certain hours of the day, or a call to a customer service phone number may keep the customer on hold.
- While images on a web page can provide a good sense about a product, it’s different from experiencing it “directly,” such as playing music on speakers, assessing the picture quality of a television or trying on a shirt or dress. E-commerce can lead consumers to receive products that differ from their expectations, which leads to returns. In some scenarios, the customer bears the burden for the cost of shipping the returned item to the retailer.
- If a customer sees an item that he or she likes in a store, the customer pays for it and then goes home with it. With e-commerce, there is a wait time for the product to be shipped to the customer’s address. Although shipping windows are decreasing as next day delivery is now quite common, it’s not instantaneous.
- Skilled hackers can create authentic-looking websites that claim to sell well-known products. Instead, the site sends customers forfeit or imitation versions of those products -- or, simply collects customers’ credit card information.